Combating depression, making basic diagnoses, and supervising surgical operations — are just some examples of what medical AI chatbots are capable of. As the global healthcare chatbot market burgeons from an estimated $300.6 million in 2023 to a projected $1.3 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.29%, their potential seems limitless. This growth is driven by a rising demand for innovation and a need to streamline patient assessments.
Today, chatbots help with handling everything from symptom collection to scheduling, significantly reducing workloads across healthcare facilities. This technology not only boosts revenue but also enhances operational efficiency and patient engagement.
In this article, we’ll examine the underlying technologies behind medical AI chatbots, as well as benefits, use cases, and steps to build such a bot. Let’s dive in!
Types of AI for medical chatbots
A medical practice chatbot is software that can communicate with patients like a human to provide instant help and facilitate the work of medical specialists.
There are two technologies to build a chatbot for a healthcare system using AI: Conversational AI and Generative AI. They are completely different and have their own pros and cons.
Conversational AI is a technology that simulates conversation by focusing on specific tasks using a limited set of data. It's designed for direct customer service, providing personalized answers by integrating with business systems. However, it follows a rigid conversation flow with predefined responses and requires regular updates to remain effective. This makes maintenance a high effort but ensures reliable, secure, and consistent interactions, ideal for handling sensitive information in medical settings.
Conversational AI models for healthcare:
- IBM Watson excels in natural language processing, making it ideal for healthcare applications such as interpreting patient inquiries, assisting with decision support, and managing medical data integration securely.
- Amazon Lex - Using the technology behind Amazon Alexa, Amazon Lex facilitates the creation of chatbots for tasks like appointment scheduling and patient data collection, providing a natural conversational interface.
- Google Dialogflow - a Google product, that enables the development of responsive and intuitive chatbots that can engage in human-like dialogue, useful for patient interactions and handling FAQs in healthcare settings.
Generative AI, on the other hand, is much better at understanding humans and generating human-like responses (Natural Language Processing), including text and images, based on its training data. In medical chatbots, it can generate dynamic, varied responses that aren't pre-programmed, allowing for more natural conversations. It excels in understanding complex requests and can improve over time with each interaction. However, its novelty means it has some limitations which must be addressed in regulated environments like healthcare.
Generative AI models for healthcare:
- OpenBioLLM-70B - Developed by Saama AI Labs, this open-source language model is tailored for the biomedical domain, enhancing tasks from research to patient interactions.
- Med-PaLM 2 - A Google Health initiative, this large language model is fine-tuned for healthcare applications, supporting tasks like nurse handoffs and clinical documentation. This is the exact technology behind Google medical AI chatbot. Additionally, MedLM, an extension of Med-PaLM 2, is available through Google Cloud’s Vertex AI, designed for a wide range of healthcare functionalities.
- GPT-4 - While not exclusively for healthcare, GPT-4 by OpenAI can be adapted for medical applications, offering reliable medical advice and patient support when fine-tuned with healthcare data.
Now, let’s compare both technologies to see the full picture.
| Aspect |
Conversational AI |
Generative AI |
| Definition |
Technology designed to simulate human-like interactions, using a limited dataset for direct responses and integration with business systems. |
AI systems that generate new content, including text and images, based on trained data, allowing for dynamic interactions. |
| User interaction |
Identifies user intent and retrieves the closest predefined answers, offering structured interactions. |
Comprehends requests and crafts original responses, enabling more nuanced and human-like interactions. |
| Market maturity |
Mature, with established systems like AWS Lex and IBM Watson, known for reliability and predictability. |
Newer technology, still being refined and optimized, less predictable but with significant potential for advancements. |
| Pros |
- Adheres strictly to instructions - High security and compliance - Consistent quality - Efficient scalability |
- Advanced understanding of human speech - Dynamic response generation - Continuous learning and improvement - Creative and flexible interactions |
| Cons |
- Rigid conversations - Limited personalization - Struggles with subtleties - Risk of user frustration |
- Security and compliance risks - Tendency to hallucinate - Potential for bias - Complexity in integration |
It is also possible to use both technologies together to enhance experience. For example, the Watsonx AI Assistant combines conversational and generative AI to manage healthcare tasks like symptom checking and appointment scheduling efficiently. It extends its capabilities with custom-built Large Language Models to handle unexpected queries by accessing extensive health data, improving the accuracy and range of its responses, thus enhancing user experience. This integration allows healthcare professionals to focus on more complex care tasks.
Now, let’s figure out what these AI medical chatbots can do.
Use cases for AI healthcare chatbots
AI health assistants are capable of performing a variety of tasks. Let’s look at some of these applications.
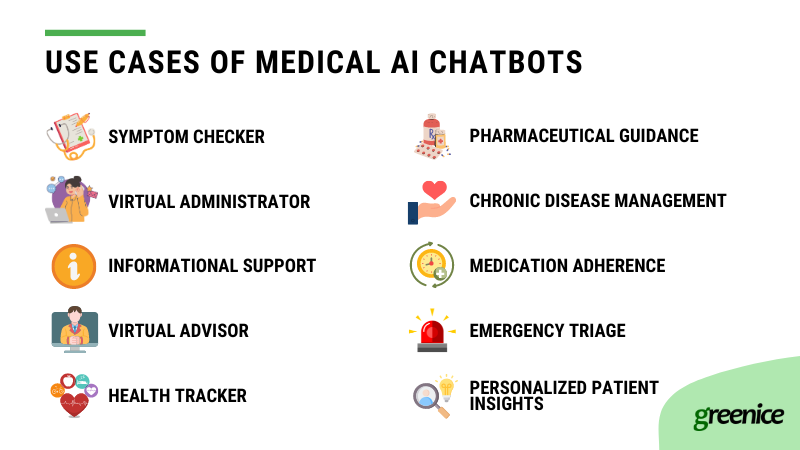
1. Symptom checker
Often people wait for appointments for several weeks before the doctor can examine them. Special chatbots can check the symptoms against a database and suggest preliminary treatment rapidly. In a way, it is an AI doctor that can provide a basic consultation online.
Ada Health is exactly such an AI-powered diagnostic bot that helps patients and doctors quickly discover the root of the problem.
2. Virtual administrator
Routine tasks such as booking an appointment, showing nearby clinics, and informing about services and procedures can be delegated to a medical office assistant chatbot that is available 24/7.
Babylon Health features an AI-powered chatbot that acts as a virtual administrator, allowing patients to book appointments, locate nearby clinics, and access medical service information at any time. This chatbot streamlines administrative tasks and enhances patient experience by providing quick and efficient responses.
Another example is a chatbot we created for one of our clients. Virtual administrator was one of the main features of this project as it helped improve customer service and reduce staff workload at the same time.
3. Informational support
Such a bot has a treasure trove of valuable information for patients, their relatives, and friends. Usually, they specialize in some particular problem or illness.
OneRemission chatbot helps cancer patients fight against their ‘enemy’ by providing tips on diet and exercise so that they can live more comfortably. OneRemissian also answers typical questions so patients do not need to visit their physician with every question.
4. Virtual advisor
In many instances, conversation is the only treatment needed, and Mental health AI chatbots excel in this role. They offer cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to address the gaps in the availability of psychological help. Often, individuals hesitate to seek mental health services due to costs, difficulty in finding specialists, or social stigma. These chatbots provide anonymous, round-the-clock support, making psychological help more accessible and immediate.
Woebot is an AI-powered mental health chatbot that effectively treats the symptoms of anxiety and depression.
5. Health tracker
Some health conditions require constant monitoring and support. A nurse chatbot can assist people who forget to take drugs or do procedures. They can be connected to wearables that measure vital signs like pulse, blood pressure, and activity. Bots will remind patients to do exercises or take medicines. They can also report progress to the physician, and provide tips on self-care to the patient.
Florence is a virtual nurse that reminds patients to take pills and check their blood pressure. It also finds the nearest doctor if necessary.
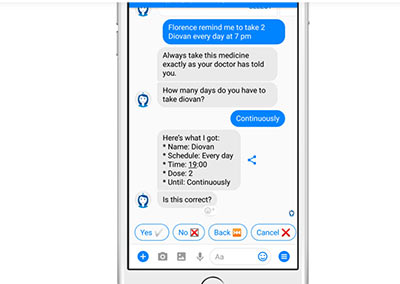
6. Pharmaceutical guidance
Doctors often need quick advice that can help them navigate through the ocean of potential medicines; instead of searching the internet, they now can take advantage of pharmacy chatbots.
For instance, Safedrugbot allows doctors to find necessary information about the use of drugs during breastfeeding (active ingredients, dangerous combinations, dosage, and alternatives).
7. Chronic disease management
Chatbots can assist patients with chronic diseases such as diabetes or hypertension by offering personalized advice, dietary recommendations, and reminders to measure blood sugar levels or blood pressure, helping them manage their conditions more effectively.
Molly (by Sensely) is a virtual health assistant powered by AI, used by healthcare providers to manage chronic diseases such as diabetes or hypertension. It interacts with patients via mobile devices, providing personalized advice, dietary recommendations, and medication reminders. Molly tracks patient data, analyzes it for insights, and helps patients adhere to their treatment plans effectively.
8. Medication adherence
These chatbots can send reminders for taking medications, provide information about drug interactions, and educate patients about the importance of adherence to their treatment plans to ensure optimal health outcomes.
MedMinder is a system designed to enhance medication adherence by sending timely reminders for medication intake, explaining side effects, and providing information on the benefits of consistent medication usage, crucial for chronic conditions.
9. Emergency triage
In emergencies, triage chatbots can quickly assess the severity of a patient’s condition based on symptoms reported and advise on the appropriate level of care needed, whether it’s a visit to the emergency room or scheduling an appointment with a specialist.
HealthTap offers an AI-powered chatbot that performs initial triage for emergency situations based on symptoms reported by the user. It assesses the severity of the condition and provides recommendations, whether it's seeking immediate emergency care or scheduling a consultation.
This feature is also integrated into our client's chatbot mentioned earlier. It assesses symptoms to determine the urgency of the case and identifies the most appropriate doctor for it.
10. Personalized patient insights
AI chatbots integrated with Electronic Health Records (EHR) can quickly provide doctors with comprehensive patient overviews, including allergies, test results, and medications. This enables the chatbot to offer personalized diagnostic and treatment recommendations based on the patient’s unique health history.
Babylon Health AI is also a good example of this. It helps in diagnosing symptoms and suggesting potential treatments, facilitating quicker decision-making for doctors and enhancing patient care.
Those mentioned above are not all possible applications of AI medical bots. New variations appear every day. Often, chatbots combine several types in one to give more value.
What type of medical chatbot is right for you?
Let's discussBut how valuable chatbots can actually be?
Benefits of an AI chatbot for healthcare
In healthcare, there can be challenges in streamlining patient interactions and enhancing service efficiency. Implementing a medical chatbot could be the solution, offering a wide range of benefits to optimize your platform’s functionality:
- No-shows reduction
For a variety of reasons, 23% of patients don’t come for their appointments. The most common causes are forgetting about the appointment and fear of procedures or diagnosis. These no-shows cost Medical companies up to $150 billion each year. A chatbot medical assistant can make the importance of the visit clear to the patient and remind them when it’s time to see a doctor.
Research says that patients feel more comfortable reporting their symptoms and emotional state to chatbots than to physicians. The chatbot can answer questions and inform patients about upcoming procedures (like colonoscopy or biopsy). They can also point to explanatory videos and reading materials.
By the way, Northwell Health launched a chatbot exactly to reduce no-shows for colonoscopies, a vital procedure in colorectal cancer diagnosis. A recent study from Nature Journal proves that an AI app for procedure preparation improves compliance which leads to a bigger number of successful colonoscopies.
- 24/7 support
Chatbots can serve thousands of people at a time, giving them immediate responses and 24-hour support. Chatbots are always polite, never get tired or irritated by repetitive questions, and attentively “listen” to each patient.
- Decrease in specialists' workload
The medical staff spends a lot of their time doing paperwork and solving administrative tasks, instead of caring for patients. Chatbots can answer questions, schedule appointments, deal with payments, help patients keep track of appointments, and perform minor procedures normally done in the hospital. This will allow medical staff to focus on helping patients, thus, reduce overwork and burnout.
- Extra medical help
The number of medical specialists is never sufficient. People who live in rural areas and those who cannot afford expensive appointments with doctors, still need help. While chatbots chatbot based on AI still cannot totally replace a real doctor, they can provide instructions for some basic treatment, help check on patients with chronic illnesses or simply remind them to take meds on time.
- Quicker and more accurate diagnostics
More intelligent chatbots can provide personalized recommendations according to the patient’s health history or symptoms. A hospital chatbot integrated with EHR can take into account patient data like allergies, analyses, and prescribed medications to quickly give doctors a full overview of the patients’ state and suggest possible diagnoses and treatments. A bot can make it easier to look up alternative medicine, proper dosage, and potentially harmful combinations. This significantly reduces the time that a doctor would normally spend to find all the necessary information.
- Health supervision
Doctors serve many people and cannot physically keep an eye on each patient. Chatbots can monitor every patients’ health condition daily, remind them to take medicine, do exercises, keep records, and then report to the physician.
- Cost efficiency
AI assistants significantly cut costs by automating routine inquiries and administrative tasks, eliminating the need for frequent call center contacts. By swiftly accessing necessary information, these chatbots reduce interaction handling time by 20%, resulting in substantial cost savings. This efficiency allows healthcare organizations to redirect financial resources towards improving patient care and investing in advanced technologies.
The best features of a medical chatbot
Depending on the needs of your medical organization, chatbots can have various functions: answer FAQs, communicate with patients, give recommendations, and fulfill administrative tasks.
In recent research, 400,000 U.S. physicians were surveyed about their attitude toward chatbots. Most of the respondents, 62%, saw benefits of using chatbots for medical organizations in the following areas:
Let’s talk about these and other popular chatbot capabilities.
1. Collecting patient data
One of the main responsibilities of a chatbot is to gather necessary information and make proper recommendations. All the data should be transferred to the CRM or EHR and added to the patient’s profile. This is a huge time-saver.
2. Answering FAQs
You can program your chatbot to give patients basic information such as:
- the clinic’s working hours, services, prices, and contacts,
- the location of the closest emergency point or service provider,
- clarification of the hospital admission process,
- the appointment time and laboratory analyses.
Bots can also provide educational materials, instructions on the proper use of medication, and information about how to prepare for medical procedures.
3. Booking appointments
Instead of calling the clinics and waiting for a secretary, patients can book appointments online with the help of a chatbot. If the patient is not sure which doctor is needed, a chatbot can ask additional questions to clarify the symptoms and match them with the relevant medical professional.
For one of our clients, a medical clinic, we created a chatbot with excellent scheduling functionality. Not only can patients schedule appointments, but they can also look through the profiles of available doctors and choose the one they like. The appointment time is automatically recorded into the doctor’s schedule.
4. Diagnostics
Ten patients out of 100 die because of diagnostic errors. These failures occur for many reasons including poor integration and data exchange in healthcare software, insufficient communication with patients, and deficiencies in the healthcare system. Using an AI chatbot for medical diagnosis can help with this problem. AI-powered chatbots backed by a strong medical database, and integration with EHR containing a patient’s history can give more accurate, quicker, and reliable diagnoses and suggestions.
5. Patient triage
For hospitals with huge patient numbers, it may be necessary to prioritize emergency cases. An AI chatbot can collect and analyze symptoms and assess the severity and urgency of each case. For minor cases, it can recommend basic medicine or treatment.
6. Renew prescriptions
One of the best features of the doctor chatbot is automatic medical prescription renewals. There is no need to wait for an appointment and go to the doctor just to give a prescription. Patients can simply enter their personal data and order refills remotely.
The chatbot sends a renewal request to the doctor who will approve or decline the prescription. If approved, the chatbot sends the renewal to the patient. A chatbot can connect with the pharmacy to check the availability of the drugs and order them for the patient.
7. Reminders
Reminding patients of appointments can reduce no-shows up to 90%. A chatbot can track the appointment schedule and notify patients in due time using their preferred channel — messenger, SMS, email. Reminders also can be set to notify patients about periodic checkups or necessary visits to the doctor. Chatbots can also give reminders to take medicine or to perform medical procedures.
8. Confirming leads for services
Chatbots work well in the marketing and sales departments. They can qualify leads by asking questions that will clarify the persons’ goals, and what to do next. Chatbots can enhance marketing campaigns, advertise services and inform patients of special deals and discounts.
9. Integrating with other software
To work effectively for your business, the chatbot should exchange data with other systems that your business uses — EMR/EHR/CRM for managing patients’ profiles, and accounting systems to track payments and send invoices.
10. Localization
If you have an international business, your customers need to be served in their language. Without a chatbot that uses the local language of your audience, you risk losing up to 40%, or more, of your potential customers.
11. Administration
Behind the scenes, chatbots should be orchestrated by an Admin to control processes, analyze statistics, check conversations for correctness, and resolve problems.
12. Speech recognition
Medical AI chatbots equipped with speech recognition allow patients to interact using voice commands, enhancing accessibility for those with visual impairments or mobility issues. This feature processes spoken language into text, enabling the chatbot to respond as it would to typed input, making healthcare interactions more natural and inclusive.
For example, Infermedica has launched Symptomate chatbot that can run as a voice-based app. It diagnoses users based on symptoms and gives treatment recommendations.
The set of features depends on the chatbot's purpose. Our client wanted its chatbot to gather data, book appointments, and administrate basic processes required by medical clinics. At that moment, such an assistant could be created with Amazon Lex technology.
Challenges of building an AI chatbot in healthcare
Using new technologies in Healthcare is riskier than in other industries because the stakes are so high. Most physicians (70%) do not trust chatbots when they deal with diagnostics or emergency triage assessment.
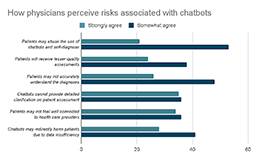
The following challenges should be addressed during chatbot creation:
a. Security breaches
Data security is one of the biggest challenges of chatbot development. Only secure data storage and channels of data transfer should be used. All data should be encrypted and available only to authorized personnel. Your chatbot must be compliant with HIPAA (for U.S. healthcare providers), GDPR (if you serve clients from the EU), and other regulations to minimize legal risks.
Special care should be taken if you use off-the-shelf solutions to create your chatbot. Unfortunately, many no-coding platforms and open-source website development solutions (like WordPress and Magento) are popular targets for hackers, who are tempted to compromise sites ‘in bulk.’
Custom websites and apps are not as tempting to ‘black hats’ as they are secured with multiple protective measures, store data on separate servers, and contain data of only one company rather than hundreds of companies (which may not be as attractive to black marketeers).
b. Ensuring the accuracy of medical information
The wrong diagnosis, misunderstanding of the diagnosis or treatment, mistakes in drug prescription, or incorrect emergency treatment may have fatal consequences. This is what physicians are afraid of most when they delegate their responsibilities to machines.
Such problems can take place due to accuracy limitations of LLMs. For example, the GPT-4 model surpasses 80% accuracy eval test by category which makes it much more reliable compared to its predecessors but not 100% bulletproof from any mistakes or so-called hallucinations. Thus, it is possible to create something similar to ChatGPT in healthcare, but it is risky.
To stay on the safe side and minimize critical errors, you should confirm to what extent you are willing to give power to chatbots. A hybrid chatbot can be a compromise solution that will send difficult questions to human agents.
How to build a healthcare AI chatbot
Now let’s talk about how to create a medical chatbot with AI functionality. Custom development is the ideal route if you're looking to create a medical AI chatbot tailored to specific healthcare requirements. Here’s a structured approach to building a chatbot that effectively supports medical professionals and patients:
1. Discovery phase
Begin by clearly defining your objectives. What goals do you aim to achieve with your medical chatbot? Which healthcare scenarios will it address? This phase involves identifying the essential functionalities your chatbot must support, such as patient intake, symptom checking, or postoperative care. The outcome of this phase should be a detailed Software Requirements Specification (SRS) that acts as a blueprint for your chatbot, ensuring it aligns with your strategic healthcare objectives.
2. Choose technology
With your goals and SRS in hand, consult with AI experts to select the appropriate technological foundation for your chatbot. This may involve choosing between solely using conversational AI for structured interactions or enhancing capabilities with generative AI through advanced models like GPT-4 or BERT, which are adept at processing and generating medical language.
3. Design the interaction model
For conversational AI, design a detailed interaction model that defines tasks, intents, and dialogue flows specific to medical contexts, such as patient history collection or appointment scheduling. This model should be iteratively refined through prototyping and user testing to ensure natural and effective communication.
4. Fine-tune with medical-specific data
If using generative AI, tailor your model by fine-tuning it with medical-specific datasets, which could include diagnostic dialogues, treatment information, and privacy-compliant patient interactions. Consider integrating retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to enhance response accuracy with domain-specific data, enabling the chatbot to provide informed and contextually relevant answers.
5. Develop an intuitive user interface
Create a user-friendly interface that facilitates smooth interactions, accommodating both text-based and voice-based queries. The interface should be designed considering the needs of diverse users, including patients, doctors, and administrative staff, across various platforms such as mobile apps and web portals.
6. Incorporate feedback loops for continuous learning
Implement feedback mechanisms that allow the chatbot to learn from real-world interactions and continuously improve. This might involve periodic retraining of the model with new data or employing reinforcement learning techniques to refine the chatbot’s responses based on user feedback.
7. Test and refine
Conduct comprehensive testing with potential end-users to identify and resolve issues in understanding, responsiveness, or accuracy. Utilize this feedback to refine the chatbot’s model, interface, and underlying natural language processing capabilities.
8. Ensure privacy and compliance
Make certain your chatbot adheres to healthcare regulations such as HIPAA in the U.S., ensuring data privacy and security. Implement strict data handling and storage protocols to protect sensitive patient information.
9. Deploy and monitor
Deploy the chatbot on your chosen platforms and monitor its performance closely. Track user satisfaction, engagement levels, and operational efficacy, ready to make iterative improvements based on ongoing feedback and insights.
10. Update regularly
Keep the chatbot’s knowledge and algorithms up to date with the latest medical guidelines, research, and user behavior trends. Regular updates are essential to maintain the relevance, accuracy, and helpfulness of the chatbot.
At each step of this journey, from the discovery phase through deployment and beyond, our team at Greenice is equipped to guide and support the development, ensuring your medical AI chatbot is robust, compliant, and effective in meeting the needs of healthcare providers and patients alike.
How to apply this to your business
Chatbots will not replace doctors either in diagnostics or inpatient care. But using a chatbot for medical clinics in combination with the traditional medical service can improve the quality of patient service, reduce medical staff burnout, and increase revenue.
Choose features that you want to see in your AI healthcare chatbot system, decide on the level of responsibility you are ready to delegate to artificial intelligence and maintain data security. Security is the most crucial element for a medical company that collects and processes sensitive patient data. To guarantee the highest level of data protection, you need to make sure that the solution you use complies with the best security practices and governmental regulations.
When choosing custom development, you may be confident data belongs only to you and no one without authorization will be able to access it. You can also modernize the solution to fit your business needs and you will not have to compromise because of limits imposed by vendors of no-code platforms.
Ready to start a new project?
Contact UsRate this article!
5
 PHP Development
PHP Development Laravel
Laravel Yii
Yii


Comments (0)