'A business without a path to profit isn’t a business, it’s a hobby'. — ‘Rework’ by the founders of 37 Signals.
If you are serious about making a profit from an online business, you need to choose a business model. This article will help you understand what a marketplace business model is and how to choose one for your startup or company. Read on!
What is the Marketplace Business Model?
Investopedia describes a business model as a company's plan for making a profit.
'They [business models] are, at the heart, stories — stories that explain how enterprises work. A good business model answers Peter Drucker’s age-old questions: Who is the customer? And what does the customer value? It also answers the fundamental questions every manager must ask: How do we make money in this business? What is the underlying economic logic that explains how we can deliver value to customers at an appropriate cost?' — wrote Joan Magretta, M.B.A., Ph.D., an award-winning contributor to the Harvard Business Review.
Since business shifted online, we have two main alternatives to brick-and-mortar stores: online stores and online marketplaces.
Online store
This business model implies that you are the only seller and make money by selling goods or services without any intermediaries.
Benefits of an online store:
- You do not need to share your profit with others
- You can start with a very simple website created with a DIY online website builder
- You have total control of the quality of your goods and services and don’t have to worry about unreliable sellers or fraudulent goods.
Challenges of an online store:
- You need to take care of serving customers: refilling goods in stock, communicating with buyers, and managing shipping and payments
- It can be difficult to scale up quickly as you will need to have plenty of liquid capital in order to maintain an adequate supply of products.
Online marketplace
An online marketplace is a web platform that works as a middleman, allowing multiple sellers to list and advertise their goods or services and sell them to the customer. As a rule, the platform owner charges a commission for each transaction and may charge other fees for the use of the platform.
Benefits of the online marketplace:
- You play the role of a mediator, not needing to worry about goods or services
- You get profit without purchasing and storing goods
- You can quickly scale up and expand your business.
Challenges of the online marketplace:
- You risk your reputation if you admit unverified vendors or buyers
- You will have to create a sophisticated website where vendors and buyers can interact easily without your help.
- Spending money upfront to build an excellent system will pay off in the long run!
And now let’s find out how to create your marketplace business model.
How to Choose a Business Model for an Online Marketplace
There are as many business models as companies because each company is unique.
To begin with, you might use the business model canvas. The concept of business model canvas was proposed in 2005 by Alexander Osterwalder of Strategyzer, a Swiss business theorist, author, speaker, consultant, and entrepreneur.
An online marketplace business model canvas can be created for any size of business — from startups with few employees to huge companies — and it allows you to get the full picture of your business model from different angles. A marketplace model canvas consists of the following nine blocks:
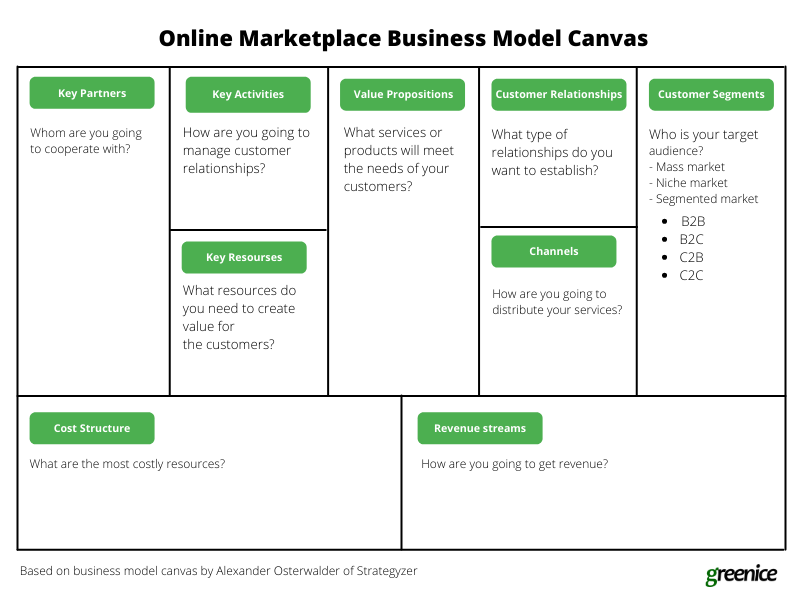
Completing this table will give you a unique business model.
You need to answer the following questions:
- Customer segments: Who is your target audience?
- Customer relationships: What type of relationships do you want to establish?
- Value proposition: What services or products will meet the needs of your customers?
- Revenue streams: How are you going to get revenue?
- Channels: How are you going to distribute your services?
- Key activities: How are you going to manage customer relationships?
- Key resources: What resources do you need to create value for your customers?
- Key partners: Whom are you going to cooperate with?
- Cost structure: What are the most costly resources?
Defining all these factors of your business will give you a business model that fits your goals exactly. Now let’s dive into the details of each component starting with the most massive ones. The description is based largely on the 2010 book ‘Business Model Generation' and adapted for marketplace business models.
1. Customer segments: Who is your target audience?
The customers can be divided as such:
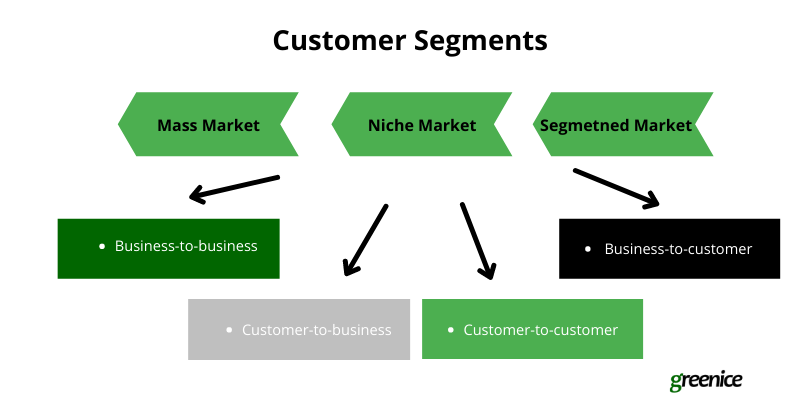
- Mass market
The mass market can be served by horizontal marketplaces, platforms that can sell absolutely any product. The benefit of running a horizontal marketplace is that you can reach a larger audience and generate more sales. On the other hand, the market is highly competitive. You’ll be going up against Amazon, Alibaba, Aliexpress, Walmart, and other local multi-vendor, online marketplaces. You must be ready to offer your customers more than your mighty rivals.
- Niche market
This audience is served by vertical marketplaces that specialize in selling products in particular niches, often very narrow. With tough competition among larger online marketplaces, startups prefer to choose online businesses with fewer competitors and less overhead. Etsy, Uber, and Airbnb are vertical marketplaces.
You can expand a vertical marketplace by adding more categories and services.
For example, Uber initially started as a peer-to-peer ride-hailing service focusing on a narrow niche. It expanded to food delivery (Uber Delivery), shipping (Uber Freight), self-driving vehicles, and ride-sharing technology (ATG).
- Segmented market
You can even narrow down your segmentation by age, gender, income, or other demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic characteristics. For example, it can be a marketplace for grandmothers who knit.
Mass, niche, and segmented marketplaces can also be divided into subtypes depending on the buyer and the seller. Here are four major types of marketplaces:
1. Business-to-business (B2B)
This type of platform connects manufacturers, wholesalers, and distributors to other businesses (end buyers and retailers). This business model is characterized by:
- Bulk ordering
- Large transactions
- Complicated transaction cycle (payments are usually processed through Letters of Credit, bank transfers, or Western Union)
- Quality control and certification (for example, buyers can order independent experts to check the quality of goods before delivery)
- Minimum order quantity
- Customization of goods and discounts for large orders
- Long-term relationships with vendors and recurring orders.
Alibaba is an example of a B2B multi-vendor marketplace online business model where overseas businesses purchase goods in bulk. The platform does not even take a commission from the transaction. Instead, the platform earns money from paid advertisements and member subscriptions.
2. Business-to-consumer (B2C)
According to this model, vendors sell the goods directly to consumers. Usually, volumes are smaller with the B2B marketplace business model and payment and delivery are quicker and easier. This online sales model is characterized by:
- Small volumes, at low prices
- Short sales cycle (one-click purchase)
- Impulse and emotional purchases
- Intense competition
Amazon marketplace business model can be described as B2C that combines direct selling of products produced by Amazon, in addition to products sold by third-party sellers through the platform.
3. Consumer-to-business (C2B)
At C2B marketplaces, individuals sell their products or services to businesses. Usually, C2B represents a service marketplace business model where specialists advertise their skills, sell their content, or look for jobs. This digital sales model is characterized by:
- Verification of the specialists' reputation
- High competition among providers
- Tracking performance
- Competition
- Ratings and reviews
The best examples of C2B marketplace models are Upwork, Fiverr, and Shutterstock.
At Upwork and Fiverr, freelancers or agencies show their portfolios and describe their skills and services, while businesses can request a quote for a certain job and hire a specialist. The marketplace owner receives a commission from the transaction.
With Shutterstock and other content creation marketplaces, authors upload their content (photos, music, texts, video, and other digital assets) and anyone can buy and use them according to the license rights prescribed by paid subscription.
We worked on another interesting creative C2B marketplace called Arcbazar. It’s the first global contest platform for designers and architects. Customers can describe what design they need, post it as a contest, and get ideas from freelance designers and agencies registered on the website. The clients choose the winner and pay them the reward in exchange for their ideas and plans.
4. Consumer-to-consumer or peer-to-peer (C2C/P2P)
The platform of this type facilitates deals between individuals. This eCommerce marketplace model is characterized by: Wide accessibility for sellers without verification Providing an enormous assortment of rare items that are difficult to locate elsewhere Difficulty to control goods and services which often leads to fraudulent deals eBay, Etsy, Airbnb, Uber, and Craigslist are some of the most famous P2P marketplaces. eBay's electronic commerce model uses auctions to provide goods at the best prices.
2. Customer relationships: What type of relationships do you want to establish?
The marketplace is a platform that acts as a middleman and regulates communication between the buyer and seller. There are several types of customer relationships that you can establish:
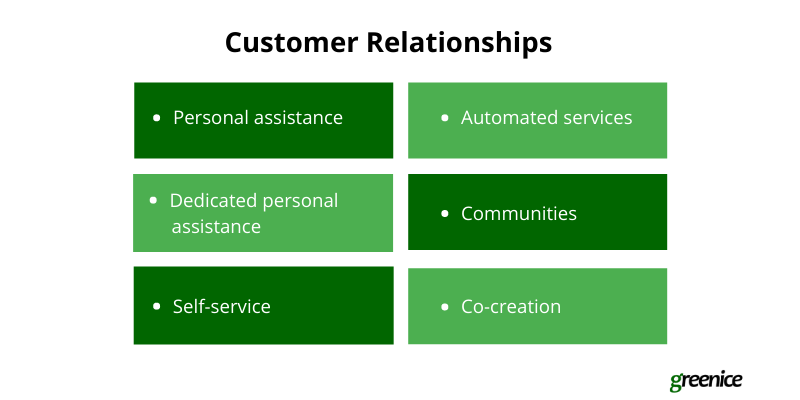
- Personal assistance: communicating with customers to help them make a purchase, and with sellers to help them create listings. The marketplace can use different messages, chats, emails, virtual assistance, and customer support.
- Dedicated personal assistance: assigning a personal sales manager to each client for personalized assistance.
- Self-service: providing customers and sellers with the necessary tools to be successful on the site. Online tutorials and FAQs can be helpful.
- Automated services: automatic suggestions based on previous purchases or preferences.
- Communities: clients help each other to solve problems and answer questions.
- Co-creation: a customer participates in the creation or improvement of the products and services.
3. Value proposition: What services or products will meet the needs of your customers?
Each year customers become more and more demanding and the competition between online services increases. New market players are forced to look for ways to stand out among rivals to win customers. You need to highlight your value proposition, and explain why your target audience should choose you instead of other guys!
How to define your value proposition? It can be tough.
Extract the essence of your platform that allows you to relieve the most acute pain of your audience. Then, wrap it in a catchy slogan that will attract attention immediately when someone opens your Homepage!
You can find a value proposition by looking at your e-business from different angles:
- your customers' pains and needs
- unique features that meet their needs
- quality of your services
- benefits for users
- advantages over competitors
Here is another canvas that will help you visualize your value proposition:
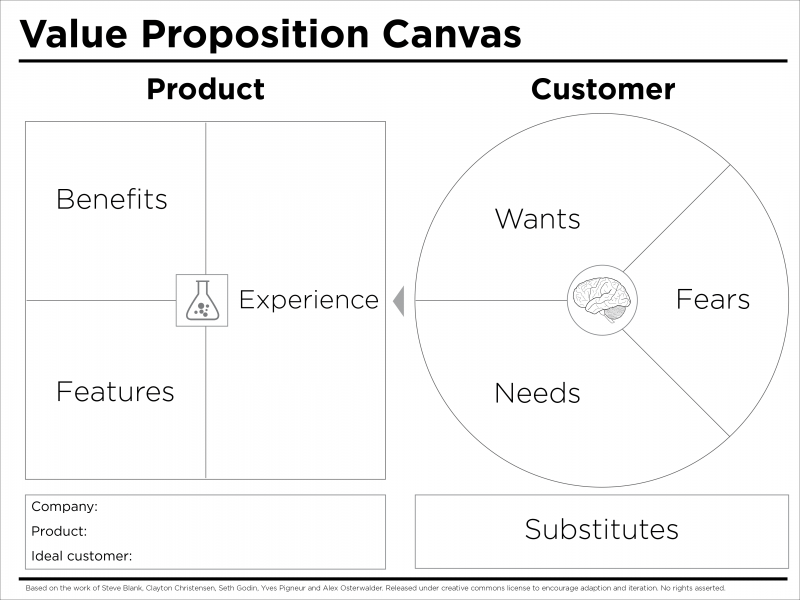
Let’s look at some examples.
Amazon's marketplace value proposition is based on low price, fast delivery, and a wide assortment of products. But Amazon also has other products — each of which has its own value proposition:
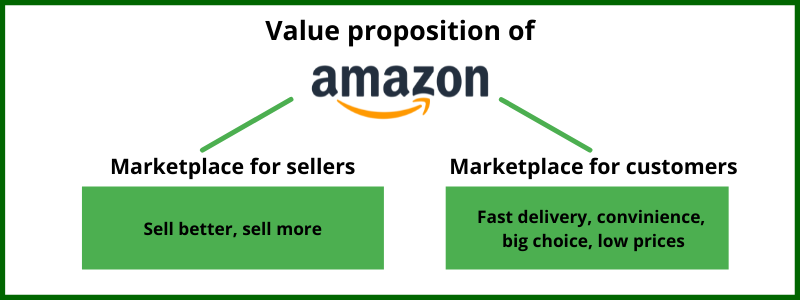
Airbnb lures travelers by promising the feeling of belonging to their destination and having an authentic 'local' experience which is incomparable to staying in a traditional, cookie-cutter hotel.

Esty offers buyers a one-of-a-kind shopping experience among unique products.

And what are your perks?
Need help with choosing a business model?
Contact UsRevenue streams: How are you going to get revenue?
There are many ways a two-sided marketplace business model can generate revenue. Let’s list the most popular options and their advantages and disadvantages:
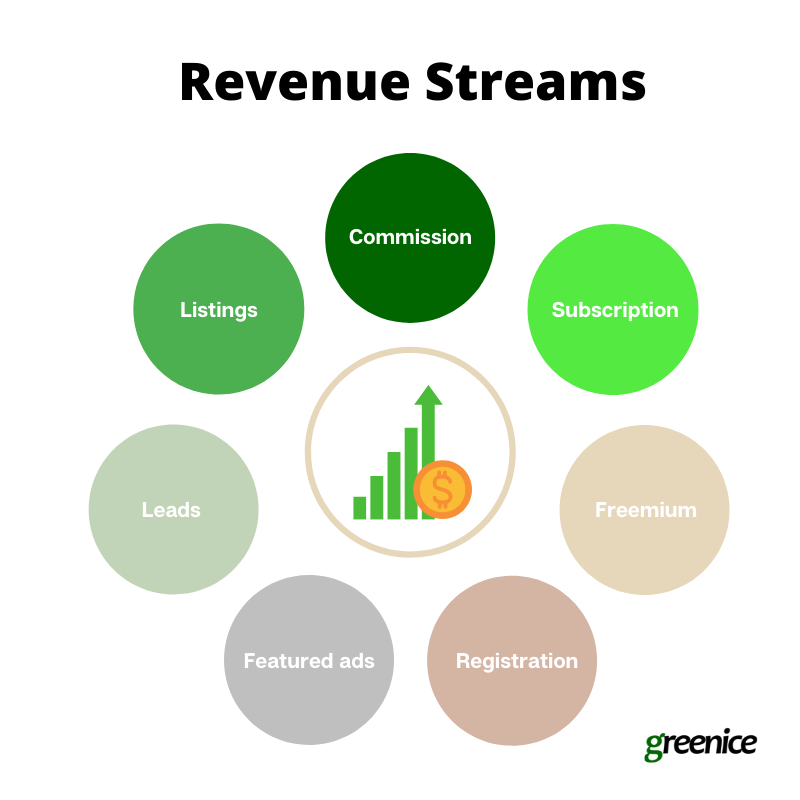
Commission
The platform takes a percentage or a fixed fee from each transaction.
To protect users from fraud, payments usually go to the platform's bank account and stay there until the buyer confirms that the goods or services were delivered.
Pros and cons of the commission-based model
| Pros |
Cons |
This marketplace financial model allows users to start without significant upfront cost, and is a fair and transparent system of payment. |
The marketplace gets revenue only when something is sold. You have to promote your marketplace all the time to attract more customers. |
Each transaction brings money to the marketplace. You can take the commission from sellers, buyers, or both — depending on your value proposition. For instance, Airbnb takes an average of 10% from hosts and 3% from guests for each booking. |
It can be difficult to come up with the appropriate fee to maintain the proper balance between being competitive and gaining profit. The range of the fees of different marketplaces varies enormously. For instance, Etsy charges only 5% of each transaction. The items presented on the platform are usually handmade, so the production cost is high — it would be senseless for artisans to give a lot of the selling price to the marketplace. A completely different model is Shutterstock, a stock-photography marketplace, where digital assets can be sold many times without added production cost. Shutterstock takes as much as 85% of each purchase on its site. |
The commission-based model has all transactions pass through the platform. Thus, all the hassle with customer verification, buyer protection, and returned products will be your responsibility. |
Subscription
Many eCommerce businesses work on a subscription basis. Users pay regularly in advance for a set of features or services.
In some cases, the subscription model is the only practical monetization method.
One example is Workaway, the peer-to-peer marketplace for homeowners who want to find volunteers that will help them with their household in exchange for a homestay, foreign language practice, or group travel. Subscription is the only sensible way to charge users because they do not book or buy anything.
A similar example is Couchsurfing, a peer-to-peer marketplace for travelers and hosts that debuted in 2003. At first, this service was free of charge. But starting in 2020, due to the Covid-19 pandemic and economic decline, the owners implemented subscription fees. Travelers are asked to pay $2 per month or $14 per year for an opportunity to find free accommodation from local hosts. As users don’t pay for lodging, no money is changing hands, so subscription is the best monetization model.
Pros and cons of the subscription-based model
| Pros |
Cons |
Independent of sales, you get regular, predictable revenue from subscription payments. |
To gain more profit, you need to attract new customers and upsell additional services and upgrades. It’s possible to combine subscriptions with other revenue methods, such as commissions. Etsy, for example, sells subscriptions, charges commissions, and will upgrade a seller's profile for a fee. |
Whether customers stay on your platform or not, you get revenue before they even start using your services. |
Few people are ready to pay for an unknown service without understanding if it fits them. One way to solve this problem is to offer a free trial period. You might also provide different subscription options with different feature sets. |
Listing fee
The marketplace takes a fee for each listing or post. There can be some free listings to allow sellers to start using your platform, but if they want to add more products or services they will have to pay. For example, in some states, Craigslist provides all functionality for free except for listings in real estate or jobs.
Pros and cons of the listing-based model
| Pros |
Cons |
Buying extra listings should not be expensive. This way, it will be more attractive for sellers than the subscription revenue model. |
As a rule, people are not motivated to pay if they can use something for free. You definitely should allow your sellers to have some listings for free, but some sellers will try to get by with only the free listings. Therefore, this eCommerce model should be combined with other revenue sources. Etsy takes listing fees while also taking a percentage from each transaction. |
Just as with the subscription, the platform earns money before a deal is made. |
Registration fee
If the platform is not going to generate a lot of money from sales, it can charge the customers for registration. However, this type of marketplace monetization can discourage users who aren’t sure if the platform fits their needs and would like to try it before buying.
Pros and cons of registration model
| Pros |
Cons |
Whether users continue using your platform or not, you have already gained revenue. |
After registering and paying, users will not send any more funds unless you combine this marketplace revenue model with others. |
Charging for sign-up is a way to take additional precautions against fake accounts and to filter out spurious users. |
Users will be more likely to pay a registration fee to join a marketplace they know, and are sure they will benefit from using. For example, such giants as Aliexpress can charge a registration fee of $1500 from sellers who create their store on the platform. |
Freemium
For those who are not sure if they want to pay for the whole functionality, there is a freemium model. It provides users free access to basic features, while advanced functions require payment. This online marketplace revenue model is more popular in SaaS business, but marketplaces also use it.
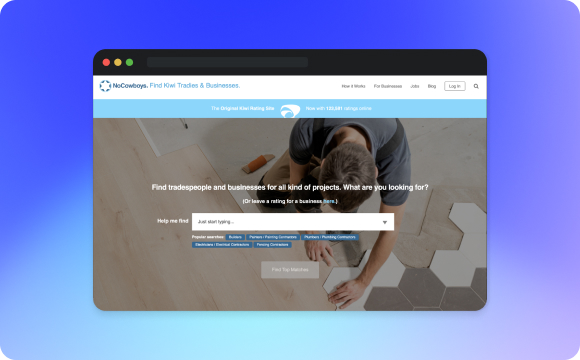
For example, for our client NoCowboys, a tradesman marketplace in New Zealand, we offered free accounts at first, and paid accounts for people who want to add photos and Google Map data, customize their profile, or have deeper analytics.
Alibaba’s sellers use the marketplace for free. But the competition is so fierce that vendors with similar goods have found a way to increase their visibility; they must upgrade to Gold Supplier status which costs several thousand dollars per year.
Pros and cons of the freemium model
| Pros |
Cons |
Using something for free is always attractive. A freemium model will attract more business. |
You need to invent indispensable, desirable features that make your freemium user pay to upgrade their account. |
Lead generation fees
With this model, the platform takes a fee for each lead or request sent to a service provider.
This is how Thumbtack works. Without taking a transaction commission, the service charges $20 per lead.
Pros and cons of lead-generation revenue model
| Pros |
Cons |
Paying a small fee for a lead can be much more profitable than paying a large commission. |
After contacting the lead, the service provider can continue further communication outside the platform and serve the clients for a lifetime without additional payments to the platform. If the seller has enough leads from the platform, they can even stop using the marketplace as they work directly with their customers and recommendations. |
This method is often criticized for unfairness and mismatching of leads to service providers, so be careful proposing it to your clients. |
Featured listings and partners ads
Sellers who want to promote their products, especially on large platforms with tough competition, will be ready to pay extra for search engine optimization or for being featured in a special section.
If you do not want to charge your users at all use sponsored ads.
Arcbazar uses this type of revenue generation. The design creators add pictures of decor and furniture right on their designs. When the customer clicks on a featured item, they are redirected to the store where they can make purchases without additional searching.
Pros and cons of ads revenue model
| Pros |
Cons |
For example, Aliexpress earns more than $7 million a year on advertisements alone. |
Even monsters like Amazon would not survive on featured ads only, so combine this method with commission or subscription revenue models. |
Here is an example from one of our projects - 4TradesOnly, a website for tradesmen recruitment. It uses a mix of revenue streams: paid ads and subscriptions. Employers (companies that hire workers) have a choice to post their job ads for free or promote them. The latter allows showing ads at the top again after the 20-day period is over. There are two paid subscription plans for employers: professional - for $15 per month and team - for $25 per month.
5. Channels: How are you going to distribute your services?
There are many channels to reach customers and deliver value to them. The main one is your marketplace and its mobile versions. You can also use social media, email, affiliate partnering, and advertising.
You can use your channels to:
- Increase the awareness of your platform
- Get customer feedback
- Deliver special deals
- Learn customer pains and preferences
- Provide customer support
To identify your channels, answer the following questions:
- What channels do you use now to approach your customers?
- How do your customers prefer to be reached?
- Are your channels integrated?
- Which channels work best?
6. Key activities: How are you going to manage customer relationships?
You should decide what services you will provide to make the interaction between the buyers and sellers as smooth as possible.
Here are some platform features:
- User Registration
- Account Creation
- Listing Creation
- Payments
- Shipping
- Returns Management
- Dispute Resolution
- Security and User Verification
- User Management
- Analytics
- Support
7. Key resources: What resources do you need to create value for the customers?
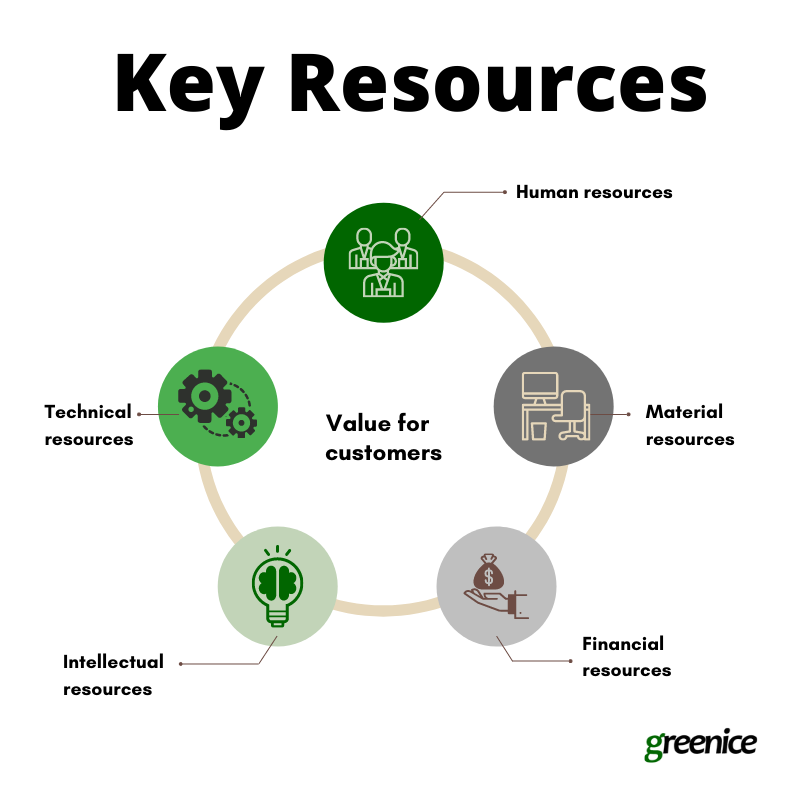
- Human resources. To create a marketplace, you need to find a development team that will implement your requirements and will stay with you in the future. Other resources include administration, customer support, accounting, and legal advice.
- Material resources. If you are a bootstrapping start-up you may start without any material resources except for your laptop. But as you scale up, you’ll probably need an office, equipment, a warehouse, and transportation.
- Financial resources. The money for implementation, marketing, maintenance, and improvement of your platform. Intellectual resources. Patents, brand trademark, software requirements specification, a database of partners and clients.
- Technical resources. Coding, web design, content of your marketplace, servers, and other infrastructure.
8. Key partners: Who are you going to cooperate with?
To strengthen your positions you may want to have partnerships with other businesses and organizations. For example, collaborate with other tech startups to add valuable features to your platform (shipping, payment gateways, identity verification), or to attract dynamic manufacturers.
For example, Etsy began as a place where individual artisans could sell their stuff. Several years ago, they created opportunities for manufacturers. The company wanted to provide an easier way for artisans to connect and collaborate with manufacturers.
9. Cost structure: What are the most costly resources?
Anticipate what expenses you will have at each stage of development. These might be:
- Marketplace development and maintenance
- Marketing and advertising
- Salaries
- Building maintenance
- Equipment and transportation cost
- Bank transactions
- Legal issues
Example of a business model canvas: ETSY
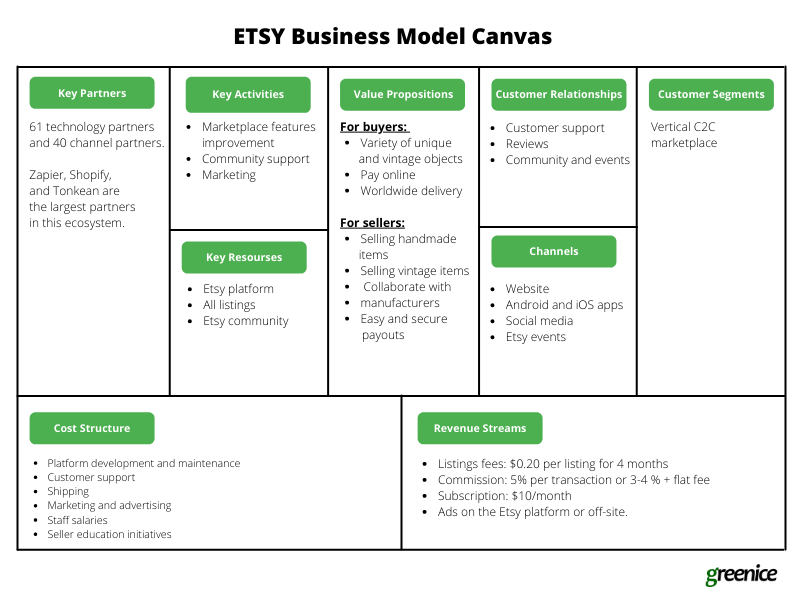
How to Apply This to Your Business
Knowing your company’s business model means having a plan for how your business will generate revenue.
Many online businesses start without verifying that their idea is viable. But no business can function long without making money, so it’s important to choose the business model that will work for you.
There is no one-size-fits-all model, as each company has a unique idea. A business model canvas is a perfect tool that can help you describe your online marketplace business model in an effective and structured way. At first, it might be difficult to complete the canvas for your business, so start by analyzing your competitors' businesses and creating canvases for them as practice.
As you understand more about how it works, start thinking about monetizing your business! We will help to implement all the necessary technical solutions to turn your dream into reality!
Do you need a monetization for a website or web app?
Contact UsRate this article!
Not rated
 PHP Development
PHP Development Laravel
Laravel Yii
Yii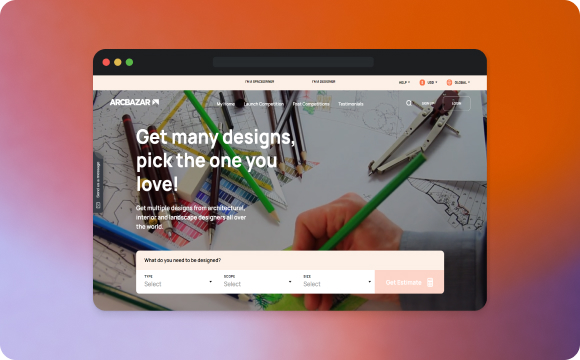



Comments (0)